07-瀑布流布局
https://www.w3cschool.cn/article/48614293.html
https://blog.csdn.net/Jzsn_Paul/article/details/140169578
https://juejin.cn/post/7368855076130488339
https://developers.weixin.qq.com/community/develop/article/doc/00004a4ae7c7a8aaddca7dc4f56413
这个瀑布流布局真的坑很多很多,还是挺难的,网上绝大部分都有瑕疵,都不能用。
- 支持下一页加载
- 高度由里面的子元素(一般为图片)高撑开
- 需要考虑图片加载慢的问题
绝对定位实现
完美实现!!!
html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{margin: 0;padding: 0;}
.main{
border: 1px solid #c1c1c1;
width: 900px;
height: 100vh;
position: relative;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.item{
width: 150px;
float: left;
}
.auxiliary{ /* 很重要,用来设置子item的margin,曲线救国 */
background: #4CAF50;
margin: 5px;
}
.item-img {
}
img { /* 一定要加这个,不然item-img的高会比img的高多几个像素 */
display: block; /* 改为块级元素 */
vertical-align: top; /* 如果仍然希望保留行内特性 */
}
</style>
<script>
function getData(curSize){
let list = []
for (let i = 0; i < curSize; i++) {
list.push(`https://picsum.photos/200/${num(100, 300)}?v=` + Math.random())
}
return list;
}
let num = (min,max) => {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * max) + min
}
function parseHTML(htmlString) {
const parser = new DOMParser();
const doc = parser.parseFromString(htmlString, 'text/html');
return doc.body.firstChild; // 返回第一个子元素
}
function insertImgToPage(src){
let app = document.getElementById("app");
let htmlString = `<div class="item"><div class="auxiliary"><div class="item-img"><img style="width: 100%" src="${src}" alt=""></div></div></div>`
const domElement = parseHTML(htmlString);
app.appendChild(domElement);
return domElement;
}
let item_ok_list = [] //已经完成瀑布流布局的图片
let g_width = 150 //全局宽度
let column; //几列
function preDeal(parent){
let cParent =document.getElementById(parent);
let p_width =cParent.offsetWidth;
column =Math.floor(p_width/g_width);
}
window.onload = function (){
preDeal('app')
}
function add(){
// 1、获取数据
let list = getData(10);
// 2、获取图片url集合
let images = list;
// 3、判断那些图片加载OK,放到数组
let completeImgList = [] //加载好的图片
// 开始加载图片
images.forEach(src => {
const img = new Image();
// 监听图片加载完成事件
img.onload = function() {
console.log(src + ' loaded');
completeImgList.push(src);
// 4、将加载好的图片插入到页面
let item = insertImgToPage(src);
// 5、瀑布流布局
pubu('app',item)
};
img.onerror = function() {
console.error(src + ' failed to load');
};
img.src = src; // 开始加载图片
});
}
let boxHeightArr =[];
function pubu(parent,child){
if (item_ok_list.length < column){
boxHeightArr.push(child.offsetHeight);
}else{
let minHeight =Math.min(...boxHeightArr);
let minIndex =boxHeightArr.indexOf(minHeight);
child.style.position ='absolute';
child.style.top =`${minHeight}px`;
child.style.left =`${g_width * minIndex}px`;
boxHeightArr[minIndex]+=child.offsetHeight;
}
item_ok_list.push(child)
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="add()"> add </button>
<div id="app" class="main">
</div>
</body>
</html>Vue3的写法
vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="addImages">Add Images</button>
<div id="myPicture" class="main" ref="appRef"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { onMounted, ref, nextTick } from 'vue';
const appRef = ref(null);
//加载OK的全部照片集合
const item_ok_list = ref([]);
//当前查看的图片
const currentPic = ref('');
// 每列的高集合
const boxHeightArr = ref([]);
//容器ID
const parentId = "myPicture"
//固定宽
const g_width = 150;
//几列
let column;
function getData(curSize) {
let list = [];
for (let i = 0; i < curSize; i++) {
list.push(`https://picsum.photos/200/${num(100, 300)}?v=` + Math.random())
}
return list;
}
let num = (min,max) => {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * max) + min
}
function insertImgToPage(src) {
const htmlString = `
<div class="item">
<div class="auxiliary">
<div class="item-img">
<img style="width: 100%;" src="${src}" alt="" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
`;
const domElement = parseHTML(htmlString);
appRef.value.appendChild(domElement);
return domElement;
}
function parseHTML(htmlString) {
const parser = new DOMParser();
const doc = parser.parseFromString(htmlString, 'text/html');
return doc.body.firstChild;
}
function preDeal() {
const cParent = document.getElementById(parentId);
const p_width = cParent.offsetWidth;
column = Math.floor(p_width / g_width);
}
onMounted(() => {
preDeal()
});
function addImages() {
const list = getData(10);
list.forEach((src) => {
const img = new Image();
img.onload = () => {
console.log(`${src} loaded`);
const item = insertImgToPage(src);
pubu(item);
// 获取实际插入到 DOM 中的 img 元素,并绑定点击事件
const imgElement = item.querySelector('img');
bindClickEvent(imgElement);
};
img.onerror = () => {
console.error(`${src} failed to load`);
};
img.src = src;
});
}
function bindClickEvent(img) {
// 绑定 click 事件
img.addEventListener('click', function(event) {
currentPic.value = event.target.src
});
}
function pubu(child) {
if (item_ok_list.value.length < column) {
boxHeightArr.value.push(child.offsetHeight);
} else {
const minHeight = Math.min(...boxHeightArr.value);
const minIndex = boxHeightArr.value.indexOf(minHeight);
child.style.position = 'absolute';
child.style.top = `${minHeight}px`;
child.style.left = `${g_width * minIndex}px`;
boxHeightArr.value[minIndex] += child.offsetHeight;
}
item_ok_list.value.push(child);
}
</script>
<style>
#myPicture {
/*border: 1px solid #c1c1c1;*/
/* background: #4CAF50;*/
width: 900px;
min-height: 600px;
position: relative;
margin: 0 auto;
/*overflow: auto;*/
}
#myPicture .item {
width: 150px;
float: left;
}
#myPicture .auxiliary {
background: #4CAF50;
margin: 5px;
}
#myPicture .item-img {
display: block;
vertical-align: top;
}
#myPicture img {
display: block;
vertical-align: top;
}
/**隐藏滚动条*/
#myPicture::-webkit-scrollbar {
width: 0.5em;
}
#myPicture::-webkit-scrollbar-track {
background-color: transparent;
}
#myPicture::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb {
background-color: transparent;
}
</style>css+js实现
实现1
非常完美

html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>瀑布流布局</title>
<style>
/* 重置样式 */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f8f8f8;
}
/* 瀑布流容器 */
.waterfall {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
padding: 10px;
}
/* 每一列的样式 */
.column {
flex: 1;
min-width: 45%; /* 两列布局,留一些间距 */
margin: 0 5px;
}
/* 每个卡片项的样式 */
.card {
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
overflow: hidden;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
/* 图片容器 */
.card img {
width: 100%;
display: block;
border-radius: 8px 8px 0 0;
object-fit: cover;
}
/* 骨架屏占位符 */
.card .skeleton {
width: 100%;
height: 200px; /* 假设图片高度为200px */
border-radius: 8px 8px 0 0;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #f0f0f0 25%, #e0e0e0 50%, #f0f0f0 75%);
background-size: 200% 100%;
animation: loading 1.5s infinite;
z-index: 1;
}
/* 标题样式 */
.card .title {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #333;
}
/* 骨架屏动画 */
@keyframes loading {
0% {
background-position: 200% 0;
}
100% {
background-position: -200% 0;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="waterfall">
<!-- 第一列 -->
<div class="column" id="column1"></div>
<!-- 第二列 -->
<div class="column" id="column2"></div>
</div>
<script>
// 模拟数据
const data = [
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/300", title: "标题1" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/100", title: "标题2" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/500", title: "标题3" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/200", title: "标题4" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/300", title: "标题5" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/400", title: "标题6" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/500", title: "标题3" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/200", title: "标题4" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/300", title: "标题5" },
{ image: "https://picsum.photos/300/400", title: "标题6" },
];
// 获取列元素
const column1 = document.getElementById("column1");
const column2 = document.getElementById("column2");
// 动态加载卡片
data.forEach((item, index) => {
// 创建卡片
const card = document.createElement("div");
card.className = "card";
// 图片部分(骨架屏占位符)
const imageContainer = document.createElement("div");
imageContainer.className = "skeleton";
card.appendChild(imageContainer);
// 标题部分
const title = document.createElement("div");
title.className = "title";
title.textContent = item.title;
card.appendChild(title);
// 动态加载图片
const img = new Image();
img.src = item.image;
img.onload = () => {
// 图片加载完成后替换骨架屏
imageContainer.replaceWith(img);
};
// 根据索引决定添加到哪一列
if (index % 2 === 0) {
column1.appendChild(card);
} else {
column2.appendChild(card);
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>实现2
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<!-- 适配移动端 -->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>小红书瀑布流布局</title>
<style>
/* 全局样式,去除默认的内外边距 */
body {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f4f4f4;
}
/* 瀑布流容器样式 */
.waterfall-container {
/* 列数为 2,实现一行两列布局 */
column-count: 2;
/* 列之间的间距为 10px */
column-gap: 10px;
padding: 10px;
}
/* 卡片样式 */
.card {
/* 防止卡片跨列显示 */
break-inside: avoid;
background-color: #fff;
border-radius: 8px;
/* 卡片阴影效果 */
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
margin-bottom: 10px;
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
}
/* 图片样式 */
.card img {
width: 100%;
height: auto;
display: block;
}
/* 标题样式 */
.card-title {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 14px;
line-height: 1.4;
}
/* 骨架屏样式 */
.skeleton::before {
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
background: linear-gradient(90deg, #f0f0f0 25%, #e0e0e0 50%, #f0f0f0 75%);
background-size: 200% 100%;
animation: loading 1.5s infinite;
z-index: 1;
}
/* 骨架屏动画 */
@keyframes loading {
0% {
background-position: 200% 0;
}
100% {
background-position: -200% 0;
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 瀑布流容器 -->
<div class="waterfall-container">
<!-- 卡片示例 -->
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/800/400" alt="Image 1" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第一张图片的标题</div>
</div>
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/300/350" alt="Image 2" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第二张图片的标题</div>
</div>
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/300/450" alt="Image 3" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第三张图片的标题</div>
</div>
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/300/300" alt="Image 4" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第四张图片的标题</div>
</div>
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/300/800" alt="Image 4" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第五张图片的标题</div>
</div>
<div class="card skeleton">
< img src="https://picsum.photos/300/200" alt="Image 4" onload="this.parentNode.classList.remove('skeleton')">
<div class="card-title">这是第六张图片的标题</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>grid实现
实现一
先看一个小demo,看似看不错,其实有很大的问题,这个高度不是动态的,是写死的。我们想要的是高度是由里面的子元素的高撑开的。

html
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport"
content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.main {
background: #e4e4e4;
display: grid;
width: 300px;
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr); /*指定两列,自动宽度*/
grid-gap: 1px; /*横向,纵向间隔*/
grid-auto-flow: row dense; /*是否自动补齐空白*/
grid-auto-rows: 20px; /*base高度,grid-row基于此运算*/
}
.main .item {
width: 100%;
background: #222;
color: #ddd;
}
.main .item:nth-of-type(3n+1) {
grid-row: auto / span 5;
}
.main .item:nth-of-type(3n+2) {
grid-row: auto / span 6;
}
.main .item:nth-of-type(3n+3) {
grid-row: auto / span 8;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="main">
<div class="item">1</div>
<div class="item">2</div>
<div class="item">3</div>
<div class="item">4</div>
<div class="item">5</div>
<div class="item">6</div>
<div class="item">7</div>
<div class="item">8</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>实现二
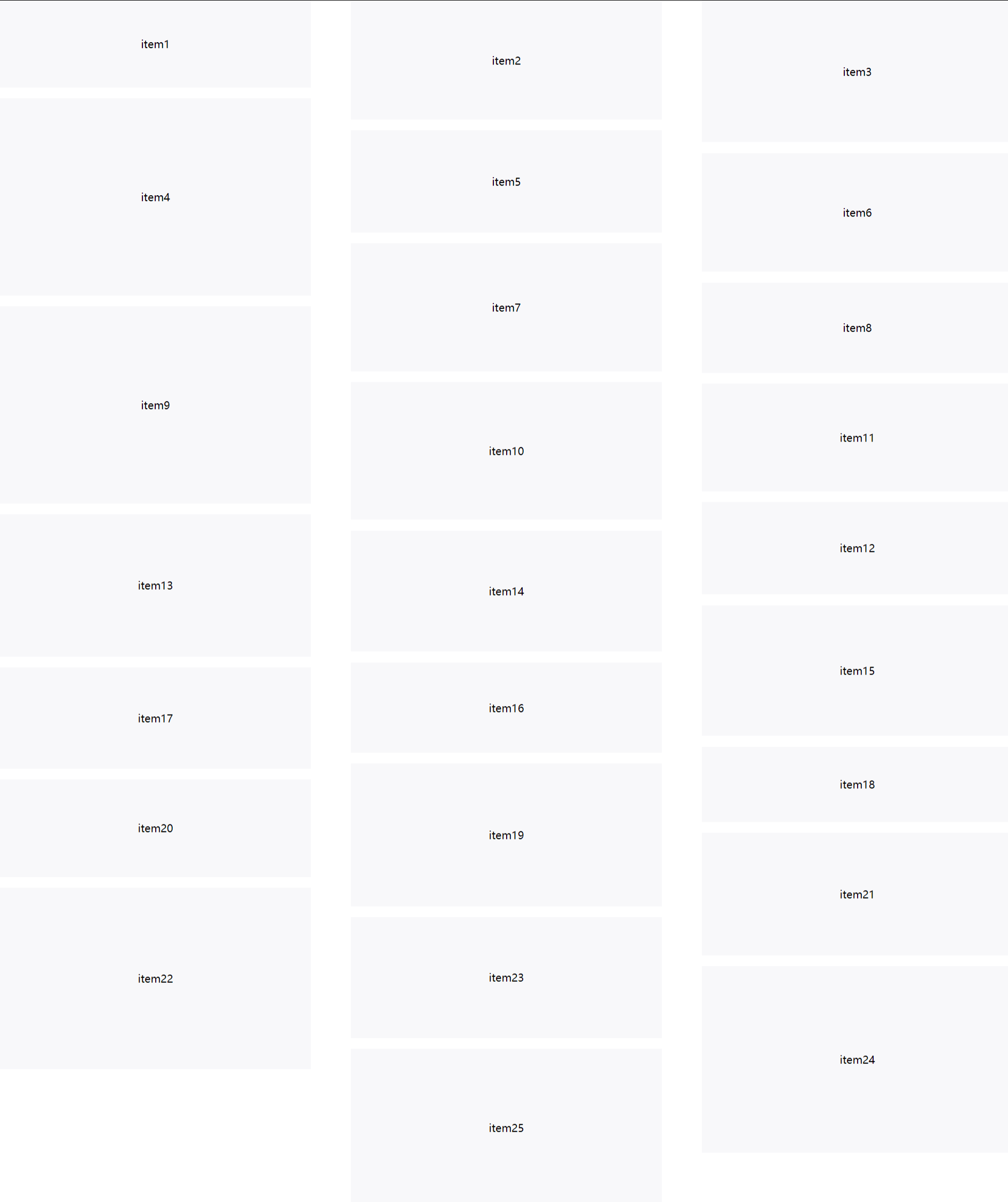
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Demo</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.masonry {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(4, 1fr);
grid-gap: 0 60px;
grid-auto-rows: 2px;
align-items: end;
}
.item {
background: #f8f8fa;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
@media (min-width: 1280px) and (max-width: 1920px) {
.masonry {
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);
}
}
@media (min-width: 768px) and (max-width: 1280px) {
.masonry {
grid-template-columns: repeat(2, 1fr);
}
}
@media (max-width: 768px) {
.masonry {
grid-template-columns: repeat(1, 1fr);
}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="masonry">
<div class="item">item1</div>
<div class="item">item2</div>
<div class="item">item3</div>
<div class="item">item4</div>
<div class="item">item5</div>
<div class="item">item6</div>
<div class="item">item7</div>
<div class="item">item8</div>
<div class="item">item9</div>
<div class="item">item10</div>
<div class="item">item11</div>
<div class="item">item12</div>
<div class="item">item13</div>
<div class="item">item14</div>
<div class="item">item15</div>
<div class="item">item16</div>
<div class="item">item17</div>
<div class="item">item18</div>
<div class="item">item19</div>
<div class="item">item20</div>
<div class="item">item21</div>
<div class="item">item22</div>
<div class="item">item23</div>
<div class="item">item24</div>
<div class="item">item25</div>
</div>
<script>
// 给每个元素模拟随机高度
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
document.querySelectorAll('.masonry > .item').forEach(item => {
item.style.height = `${Math.floor(Math.random() * 200) + 100}px`
})
})
const calcRows = () => {
const masonry = document.querySelector('.masonry')
const items = masonry.querySelectorAll('.item')
// 获取当前列数 这个API可以直接使用,grid专门提供的
const cols = getComputedStyle(masonry).gridTemplateColumns.split(" ").length;
items.forEach((item, index) => {
// 给需要上下间隔的元素增加上间隔(每列第一个元素无需上间隔)
const gapRows = index >= cols ? 8 : 0;
// 根据元素高度设置元素的需占行数
const rows = Math.ceil(item.clientHeight / 2) + gapRows;
item.style.gridRowEnd = `span ${rows}`;
})
}
window.addEventListener('resize', calcRows)
window.addEventListener('load', calcRows)
</script>
</body>
</html>实现无限滚动
主要是利用了IntersectionObserver这个API的能力,检测目标dom是否出现在容器的视口中
描述: 定义了在目标元素与根相交时,触发回调的可见性阈值,范围在 0 到 1 之间。
threshold:
- 0 表示只要有任何部分可见,回调就会触发;
- 1 表示目标元素全部可见时才会触发。
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Intersection Observer Demo</title>
<style>
#container {
height: 200px;
overflow: auto;
border: 1px solid #000;
}
#target {
height: 100px;
background-color: lightblue;
margin-top: 300px; /* initial position is outside of the viewport */
}
.spacer {
height: 500px; /* create space to scroll */
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="container">
<div class="spacer"></div>
<div id="target">Target Element</div>
</div>
<script>
const target = document.getElementById('target');
const container = document.getElementById('container');
const options = {
root: container, // 观察的上下文元素
rootMargin: '0px',
threshold: 0.1 // 目标元素在根元素中可见的百分比时触发
};
const callback = (entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach(entry => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
// 元素出现在容器内,触发事件
console.log('Target is inside the container!');
// 这里可以执行更多的逻辑,比如调用其他函数等
// 如果你只希望触发一次事件,可以取消观察
observer.unobserve(entry.target);
}
});
};
const observer = new IntersectionObserver(callback, options);
observer.observe(target); // 开始观察目标元素
</script>
</body>
</html>
